Overview
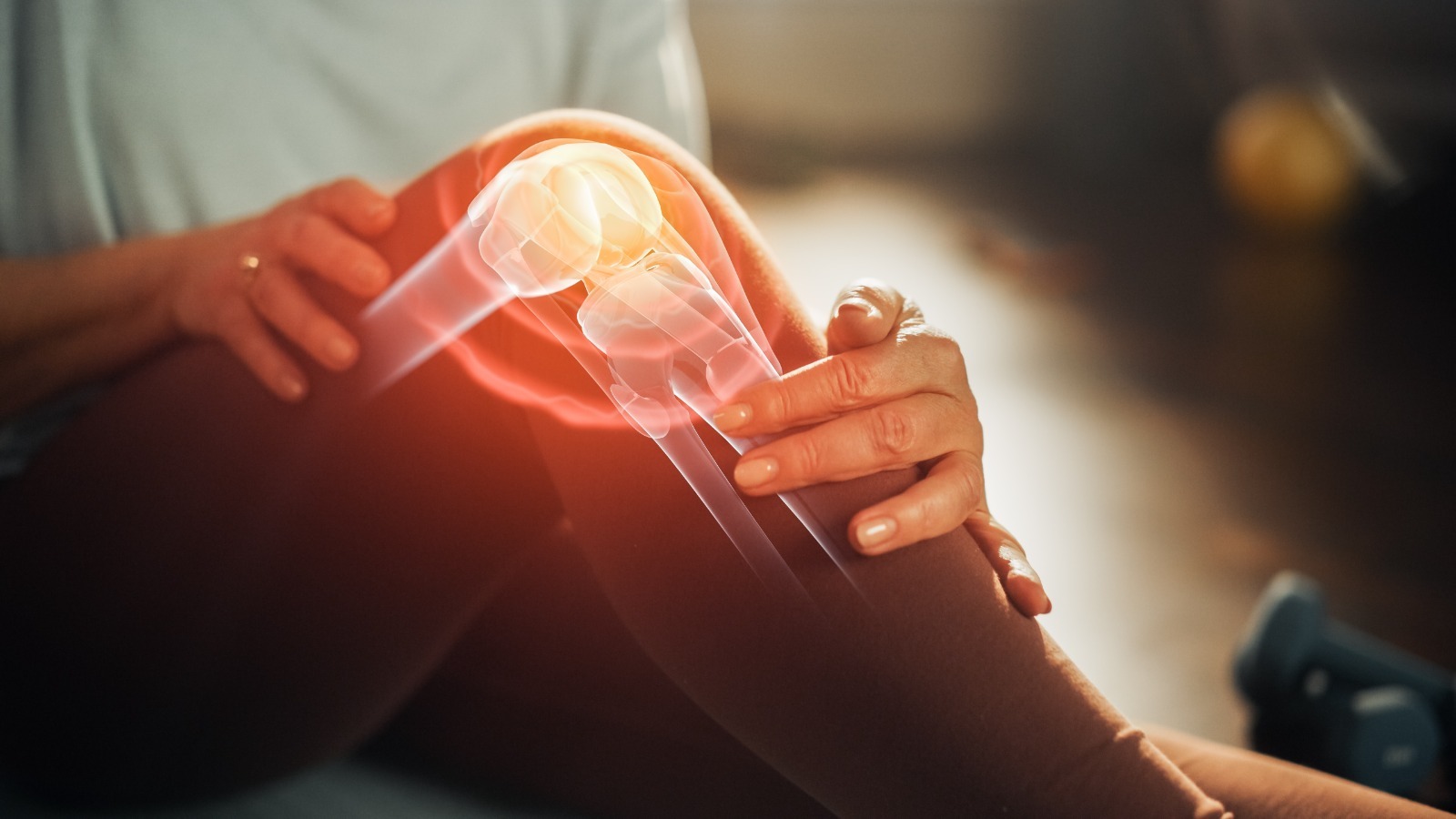
Knees and hips are the most functional and weight-bearing joints in our body;
Many diseases like osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis affect the functionality of the joint, especially the knee joint. This can significantly lower the quality of life and interfere with usual day-to-day activities;
Fall and fractures may severely damage the hip joint which unfortunately leads to severe pain, immobility and loss of function of the joint.
What causes the pain and loss of functionality
Cartilage Loss: In a healthy knee or hip join, smooth cartilage covers the ends of the bones, cushioning them and allowing easy, pain-free movement. In conditions like osteoarthritis, this cartilage wears away, leaving the bones to rub against each other, which causes pain, swelling, and stiffness.
Bone Spurs: When cartilage wears down, the body may try to repair the damage by forming small bony growths called bone spurs (osteophytes). These can create friction within the joint and contribute to pain and limited movement.
Joint Inflammation: As the cartilage breaks down, inflammation can occur, leading to swelling and further irritation of the surrounding tissues, which makes the joint feel painful, especially with movement.
Nerve Irritation: Constant wear on the knee joint can also lead to irritation or compression of nerves around the knee, which may cause sharp or shooting pains.
What happens if the problem is not addressed
-
- Chronic Pain: Ongoing joint damage usually leads to persistent, sometimes severe pain, which can impact daily activities like walking, standing, and even sitting for extended periods. Over time, this pain can become more difficult to manage with medication alone.
-
- Limited Mobility: As joint deterioration progresses, range of motion decreases, making it harder to bend, extend, or rotate the joint fully. This limitation can restrict movement and make everyday tasks, like climbing stairs or getting in and out of a chair, increasingly difficult.
-
- Loss of Muscle Strength: Reduced mobility and chronic pain can lead to less physical activity, which in turn causes muscle weakness, particularly around the affected joint. This weakness can make the joint less stable and worsen mobility problems.
-
- Joint Deformity: In advanced stages, the joint may become deformed due to misalignment of the bones, cartilage loss, or the formation of bone spurs. This can change the leg’s shape, making walking even more challenging and painful.
-
- Increased Risk of Falls: Limited mobility, pain, and joint instability can increase the risk of falls. Falls are particularly dangerous for older adults and can lead to fractures or additional injuries.
-
- Impact on Mental Health: Chronic pain and limited mobility can lead to frustration, anxiety, depression, and a reduced quality of life. Social isolation and decreased participation in enjoyable activities are also common, impacting emotional well-being.
-
- Strain on Other Joints: When one joint, like the knee or hip, isn’t functioning properly, it places extra strain on other parts of the body. For example, an injured knee may lead to overuse of the other knee or the hips and lower back, potentially causing additional pain and joint problems over time.
In such cases, a surgery can be a gamechanger.
The goal of the surgery (Arthroplasty) is to replace or remodel the damaged joint to regain and restore the joint function and dramatically decrease pain.
Knee and hip replacement surgeries give you an opportunity to prolong your life by gaining back your functionality and living a full life without the burden of the disease;
Procedure
During the surgery (called arthroplasty) the damaged knee/hip joint is replaced with an artificial one.
Knee replacement: Knee replacement is done with the use of general anesthesia (meaning you will be completley uncoscious during the operation); During the procedure surgeon makes an incision over the damaged knee, removes the knee cap (patella) and smoothes the end of the thigh bone (femur) and shinbone (tibia) so that the artificial joint (prosthesis) is attached more easily; The parts of prosthesis then are inserted into the thigh bone and shinbone and cemented into place;
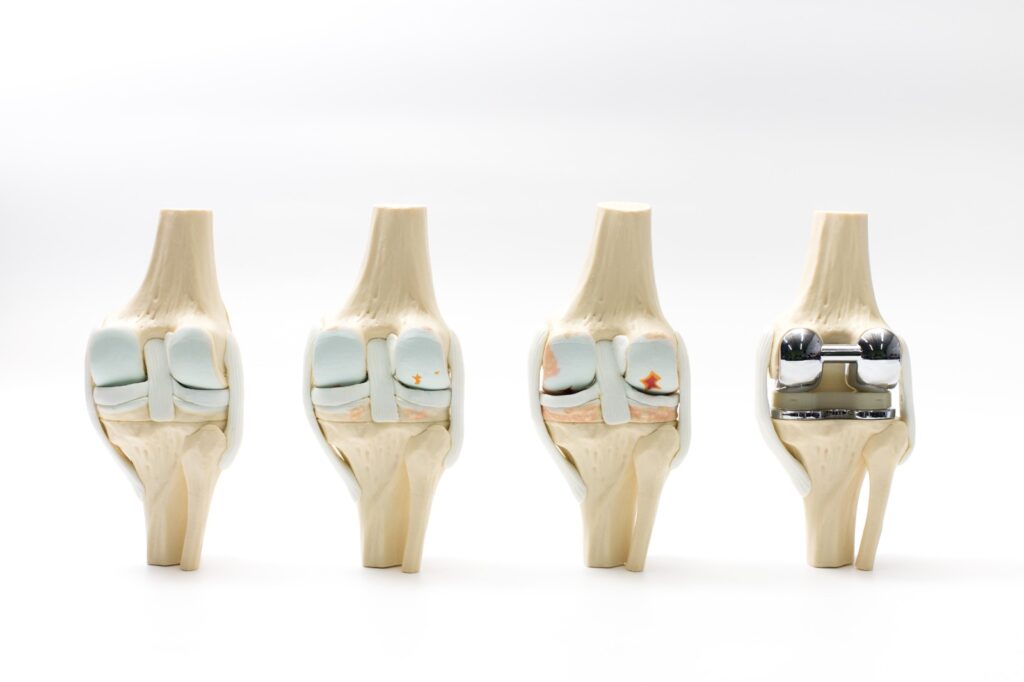
Hip replacement: All or part of the hip may be replaced;
-
- Partial hip replacement (partial hip arthroplasty) – The damaged top part of the thigh bone (femur) is replaced with a prosthesis made out of metal.
-
- Total hip replacement (total hip arthroplasty) – When the surface of the socket where the head of thigh bone sits is also damaged the socket is replaced as well with a metal shell lined with a durable plastic.
| Knee replacement | Hip replacement | |
|---|---|---|
| Avg. Hospital Stay | 1-3 Days | 3-5 Days |
| Avg. Time off-work | 4-6 Weeks | 2 Weeks |
| Operating time | 1-2 Hours | 1-2 Hours |
| Risks of Complications | Seriour complications are rare. Potential compoilcations include infection, blood clots, implant loosening or failure, nerve or blood vessel damage, persistent pain or stiffness, and, in rare cases, adverse reactions to anesthesia. | Serious complications are rare. Potential compoilcations include infection, blood clots, implant loosening or failure, nerve or blood vessel damage, persistent pain or stiffness, and, in rare cases, adverse reactions to anesthesia. |
Expected price ranges with our clinics:
| Knee Replacement | Hip replacement | |
|---|---|---|
| Higher Budget Options | $11,500 – $16,500 | $11,500 – $16,500 |
| Mid Budget Options | $9,000 – $9,700 | $8,500 – $9,800 |
| Lower Budget Options | $6,499 – $9,000 | $6,499 – $8,500 |
The below picture demonstrates how the two joints will look after the surgery:
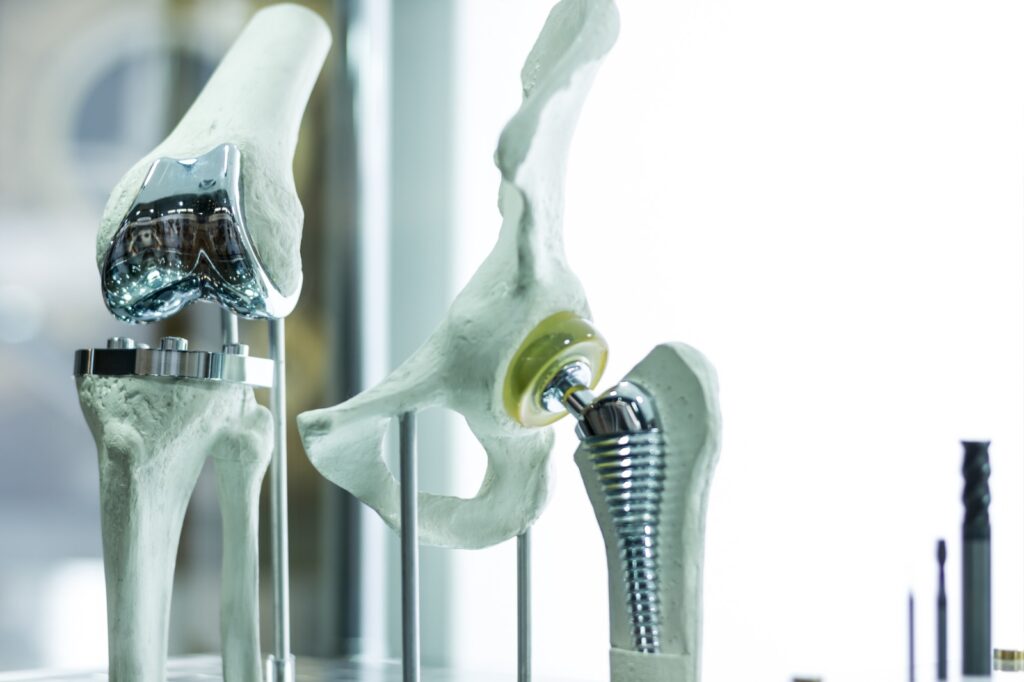
Before the surgery
There are many different types of prosthetics are available for knee and hip replacement;
Prior to surgery the doctor and their team will discuss what the best options are for you and your specific needs.
The tests done before the surgery include – x-ray of the affected joint and their healthy counterpart; electrocardiography, blood tests;
Post-surgery considerations Hospital stays last for 1-3 days after knee replacement and 3-5 days after hip replacement surgeries; Recovery nowadays is faster with the help of physiotherapy and patients are encouraged to start walking as soon as possible after the procedure; But keep in mind that return to normal daily activities with usual intensity may take several weeks and full recovery will take months.